Financial Statements of Cooperative Society

The financial statements of a cooperative society are some of the important documents that present the financial status and activities of the society. These statements will aid members and regulators in informed decision-making on the basis of transparency and accountability.
Key Components of Financial Statement of Co-operative Society
Your cooperative society financial statement needs four key documents that paint a complete picture of your organization’s finances. These documents in final accounts of cooperative society help you make smart decisions about your society’s financial health and future plans.
| 1. Balance Sheet |
| 2. Income Statement |
| 3. Cash Flow Statement |
| 4. Members’ Equity Statement |
1. Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet shows your cooperative society’s financial status at any given moment. The Balance Sheet lists everything you own (assets), everything you owe (liabilities), and your members’ equity (net worth). Your society’s assets usually include fixed deposits, inventory, and property, while loans and pending payments make up the liabilities.
2. Income Statement
The Income Statement, also called the Profit and Loss Statement, reveals your society’s financial performance during specific periods. This document tracks all your money sources, especially when you have membership fees, sales, and investment income. On top of that, it records expenses like operational costs, employee salaries, and administrative overhead to figure out your net profit or loss.
3. Cash Flow Statement
The Cash Flow Statement shows how money moves through your cooperative society. This document tracks three main areas:
- Operating activities (day-to-day business)
- Investing activities (purchase or sale of assets)
- Financing activities (loans and member contributions)
4. Members’ Equity Statement
The Members’ Equity Statement shows changes in your society members’ ownership stakes. This document tracks member shares, retained earnings, and statutory reserves changes. Your society needs this document to monitor Reserve Fund allocation and dividend payments effectively.
Also Read: Cooperative Society Accounting
Understanding the Cooperative Society Balance Sheet
The balance sheet in the final accounts of cooperative society displays assets, liabilities, and members’ equity at a particular point. It offers a clear snapshot of financial position, aiding in planning and compliance.
Key Components of the Co Operative Society Balance Sheet Format in Excel
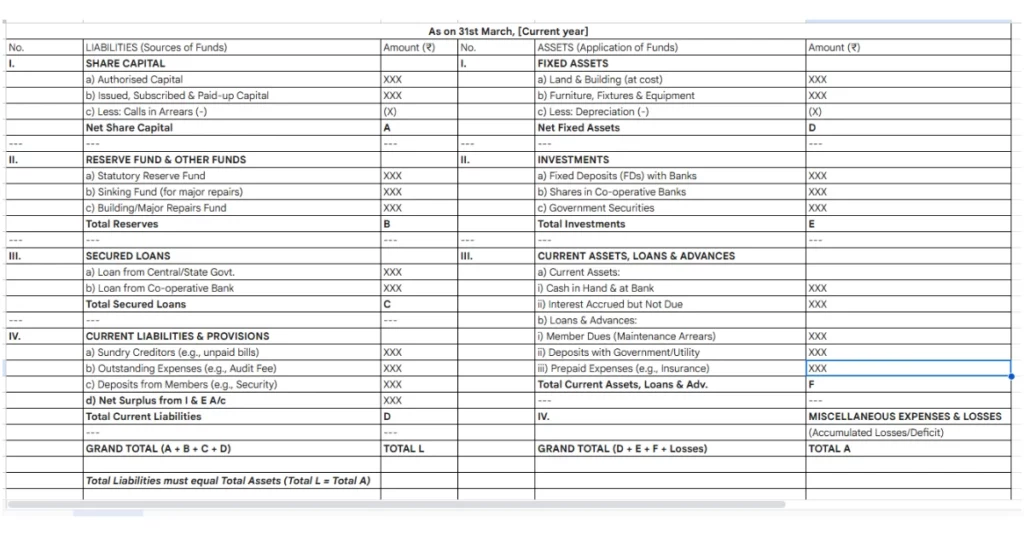
- Assets: Cash and receivables Fixed assets: Property and machinery
- Liabilities: Current liabilities include short-term loans, accounts payable.
- Equity: Members’ contributions, reserves, and retained profits
Preparing the balance sheet involves gathering financial records, listing assets, liabilities, and calculating members’ equity. Using a co-operative housing society balance sheet format in Excel simplifies this process, ensuring accuracy and uniformity.
Read more on: Housing Society Balance Sheet
Income and Expenditure Account of Cooperative Society
This statement summarizes all income and expenditures over a specific period, showing the cooperative’s surplus or deficit. It typically includes:
- Income sources: member contributions, interest earnings, and sales revenue
- Expenditure items: operating costs and interest on loans
Maintaining this account is essential for regularly assessing the cooperative’s financial performance and ensuring transparent financial management
Maintenance of this helps in accessing financial performances regularly
Read more on Income and Expenditure Account of Cooperative Society
Preparation of Financial Statements of cooperative society
Your financial statements of cooperative society need a systematic process that matches accounting standards and regulatory requirements. These statements must show your society’s true financial position and performance.
The bookkeeper logs daily transactions in a journal and moves them into the general ledger. Your accounting team creates a trial balance each month to check record accuracy. Your society needs separate trading accounts for each non-credit activity.
The reporting schedule looks like this:
| Statement Type | Preparation Frequency |
| Trial Balance | Monthly |
| Trading Account | Monthly |
| Profit & Loss Account | Monthly |
| Balance Sheet | Yearly |
The annual account closure process carries real and personal account balances forward as next year’s opening figures. The nominal account balances move to the profit and loss account. These statements help multiple stakeholders like members, management, creditors, and regulatory authorities, making compliance with accounting standards essential.
The statements become useful through four key qualities: understandability, relevance, reliability, and comparability. Members should receive these financial statements of cooperative society 14 days before the Annual General Meeting. This gives them enough time to review the figures and ask questions about the financial data.
Also Read: Housing Society AGM Meeting Rules: A Detailed Guide
Analysis of a Cooperative Society’s Financial Statement
A detailed analysis of your financial statements of cooperative society reveals strengths, weaknesses, and growth opportunities. Numbers tell a story when you look at them together rather than separately.
Financial analysis starts with key ratios that show profitability, liquidity, and efficiency. These essential ratios will give you a clear picture of your society’s performance:
| Ratio Type | What It Measures | Target Range |
| Current Ratio | Short-term financial health | 2:1 or higher |
| Debt-to-Equity | Financial leverage | Below 2:1 |
| Return on Investment | Profitability efficiency | Above 15% |
| Member Return Ratio | Benefits to members | Above 60% |
Trend analysis shows your society’s progress through the years. You can spot patterns in membership growth, profit margins, and operational efficiency by comparing current performance with past data. This information helps guide planning and resource allocation effectively.
Comparing your performance with similar cooperative societies provides valuable context. Your society’s metrics should line up with industry standards while accounting for unique factors like membership size and business focus. The full picture includes member satisfaction levels and your society’s success in meeting both social and financial goals.
Regular monitoring of these financial indicators leads to better decisions and helps your cooperative society maintain financial stability while delivering member benefits.
Best Practices in Financial Statements of Cooperative Societies
Effective accounting includes:
- Daily book-keeping and record maintenance
- Use of journals and ledgers for transactions
- Regular preparation of trial balances
- Utilizing digital tools or software for accuracy
Importance of Financial Statements for Cooperative Societies:
- Decision-making: Assists management and members in guiding future activities
- Compliance: Meets statutory and regulatory requirements
- Transparency: Builds members’ trust through clear financial disclosure
Overview: Key Financial Statements and Their Purpose
| Financial Statement | Purpose |
| Balance Sheet | Shows financial position at a point |
| Income & Expenditure Account | Records income and expenses over time |
| Receipts & Payments Account | Tracks cash inflow and outflow |
| Cash Flow Statement | Details liquidity and cash management |
Also Read: Housing Society Fund Utilisation
NoBrokerHood Society Accounting Software
NoBrokerHood accounting software is designed to simplify financial management for cooperative societies with easy-to-use features.
It helps societies maintain accurate financial statements like balance sheets and income-expenditure accounts efficiently, improving transparency and reducing manual workload. This makes NoBrokerHood an effective tool for cooperative society accounting needs
Key features:
- Automated invoice and billing generation
- Simple expense tracking and management
- Integration with Tally for accounting ease
- Management of multiple housing society bank accounts and petty cash
- Secure online payment processing
- Detailed financial reporting and auto reconciliation
All Solutions by NoBrokerHood
FAQs
A cooperative society typically prepares four key financial statements: the Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and Members’ Equity Statement. These documents collectively provide a comprehensive view of the society’s financial position and performance.
While some statements are prepared monthly, such as the Trial Balance, Trading Account, and Profit & Loss Account, the Balance Sheet is typically prepared annually. These statements should be distributed to members at least 14 days before the Annual General Meeting.
A cooperative society’s balance sheet presents a snapshot of its financial position, listing all assets (what the society owns), liabilities (what it owes), and members’ equity (net worth). This includes items such as fixed deposits, inventory, property, loans, and outstanding payments.
Members can analyze their society’s financial health by examining key ratios such as the Current Ratio, Debt-to-Equity Ratio, Return on Investment, and Member Return Ratio. Trend analysis and benchmarking against similar societies also provide valuable insights into the society’s performance.
Cooperative societies follow specific accounting principles that align with their unique structure and goals. These include cooperative principles like democratic control and fair sharing of benefits, as well as standard accounting practices to ensure transparency, relevance, reliability, and comparability in financial reporting.
They ensure transparency, help in regulatory compliance, guide informed decision-making, and build member trust.